What is the difference between the '==' and 'is' operators?
What should you do to compare two objects?
In order to compare two objects, you should start with the '==' operator as usual. This operator compares the values of both operands and checks for value equality. So here we witness a values comparison.
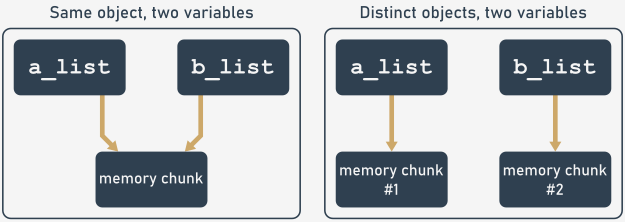
In fact, two distinct objects holding the same values could be compared, and the result would be 'True'. Moreover, when you compare two variables referencing the same object, the result would be also 'True'.
To check whether both operands refer to the same object or not, you should use the 'is' operator. In other words, it responds to the question: “Are both variables referring to the same identity?”
Run the code presented in the editor.
The output is:
a_string identity: 3687888
b_string identity: 3687888
The result of the value comparison: True
The result of the identity comparison: True
a_string identity: 3689048
b_string identity: 9418632
The result of the value comparison: True
The result of the identity comparison: False
output
This could be depicted as follows:
Code
a_string = ['10', 'days', 'to', 'departure']b_string = a_string
print('a_string identity:', id(a_string))
print('b_string identity:', id(b_string))
print('The result of the value comparison:', a_string == b_string)
print('The result of the identity comparison:', a_string is b_string)
print()
a_string = ['10', 'days', 'to', 'departure']
b_string = ['10', 'days', 'to', 'departure']
print('a_string identity:', id(a_string))
print('b_string identity:', id(b_string))
print('The result of the value comparison:', a_string == b_string)
print('The result of the identity comparison:', a_string is b_string)