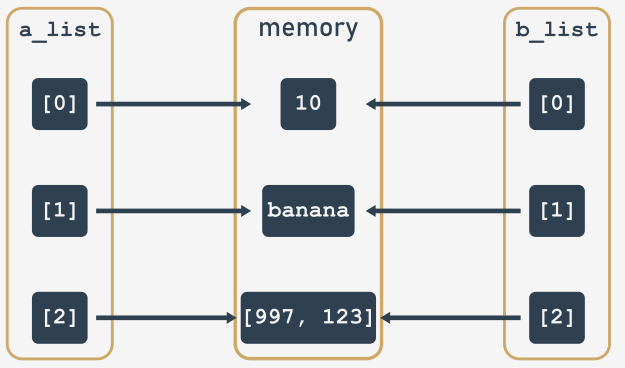
The explanation of the behavior presented on the previous page is:
- the
'a_list'object is a compound object; - we’ve run a shallow copy that constructs a new compound object,
b_listin our example, and then populated it with references to the objects found in the original; - as you can see, a shallow copy is only one level deep. The copying process does not recurse and therefore does not create copies of the child objects, but instead populates
b_listwith references to the already existing objects.